Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a thin layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from its normal position.
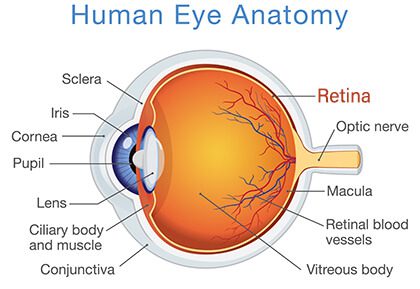

Retinal detachment separates the retinal cells from the layer of blood vessels that provides oxygen and nourishment. The longer retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater your risk of permanent vision loss in the affected eye.


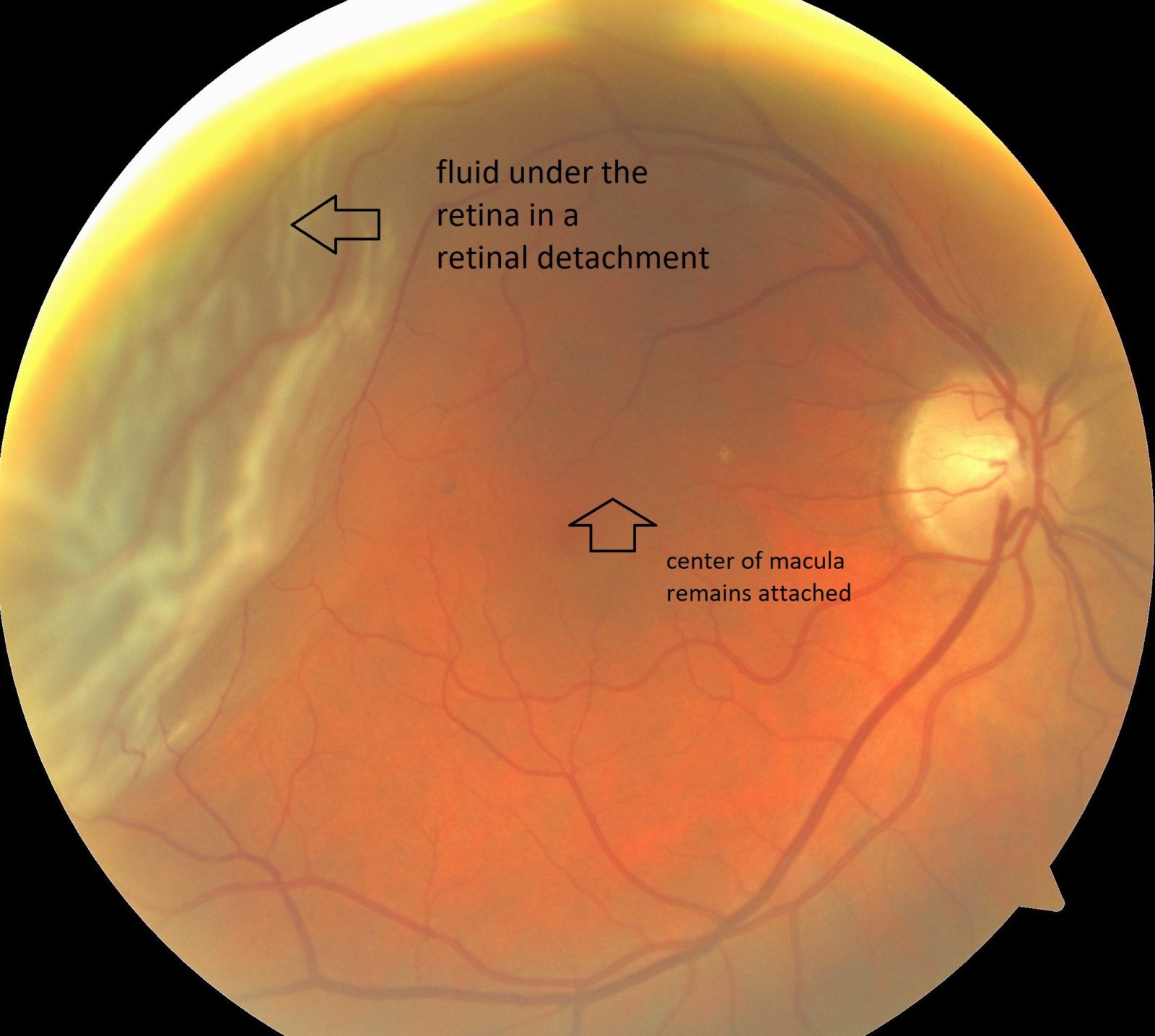
Warning signs of retinal detachment may include one or all of the following: the sudden appearance of floaters and flashes and reduced vision. Contacting an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) right away can help save your vision.

Symptoms
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as:
- The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
- Blurred vision
- Gradually reduced side (peripheral) vision
- A curtain-like shadow over your visual field
Treatment: Surgery
- Laser retinopexy


- Vitrectomy

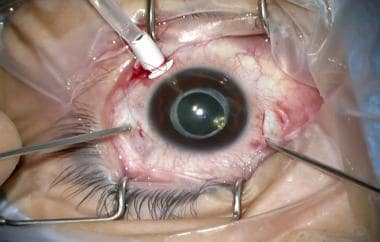
- Cryopexy

- Scleral Buckling
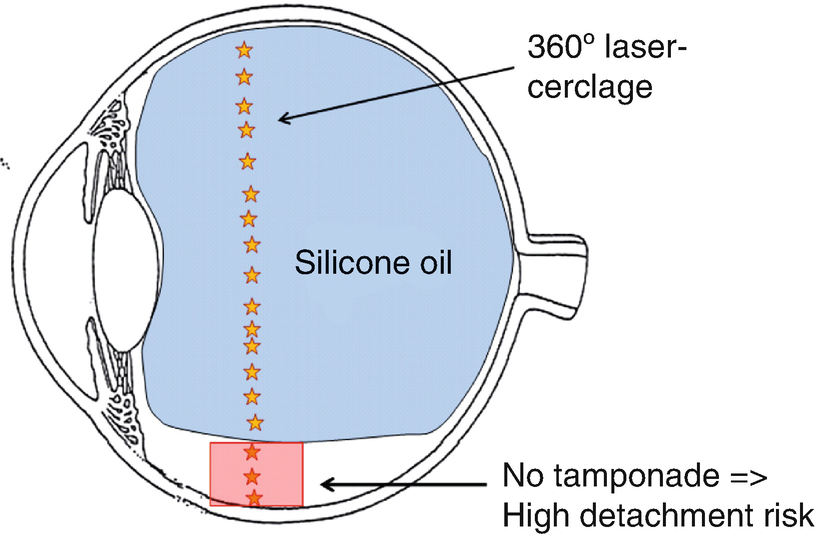
- Gas tamponate.

- Oil tamponate

留言
張貼留言